Types Of Heat Loss Anesthesia
Heat loss is proportional to the surface area exposed. It also has antiemetic actions and recovery is not delayed after prolonged infusion.
There are four main types of anesthesia used during medical procedures and surgery and the potential risks vary with each.

Types of heat loss anesthesia. To evaluate the efficiency of four warming procedures introduced after anaesthetic induction and continued during surgery in minimising heat loss in anaesthetised dogs. Propofol produces anesthesia in 1545 seconds as rapidly as intravenous barbiturates but patients recover faster. It is important to remember that vasodilation caused by gas inhalants is dose dependent.
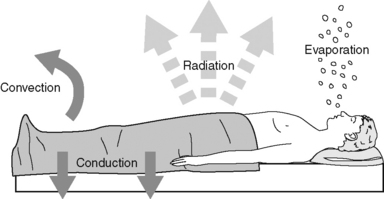
The amount of heat loss from convection is dependent upon the airflow or in aquatic exercise the water flow over the skin. During anesthesia and surgery however heat loss is often far greater. However each subsequent layer of insulation is less and less effective.
Which anatomical structure regulates temperature by monitoring processes of heat production and loss in the human body. Because of increased evaporative heat loss hypothermia is also more likely to occur if the skin of the patient is wet or comes in contact with wet drapes. The opposite is hypothermia which occurs when the temperature drops below that required to maintain normal metabolism.
Ninety-six dogs were involved in total. Patients under anesthesia typically do not sweat which is the main way that heat is lost due to evaporation. Newer opioids such alfentanil and remifentanil have been used for the induction of anesthesia.
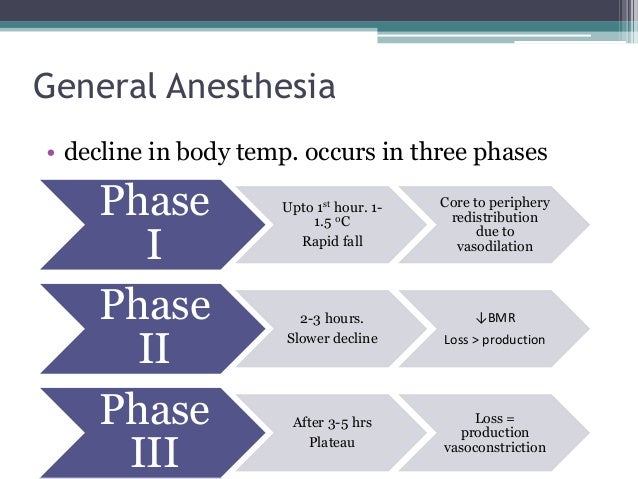
Two mechanisms of undesired heat loss in the OR. Obviously respiratory heat loss increases if the patient breathes cool dry air as opposed to warm moisturized air Bissonnette et al 1989a 1989b. Patients with an autonomic neuropathy diabetics have impaired sympathetic vasoconstriction and are unable to establish a core plateau in phase 3.
Blankets plastic sheeting etc are effective. The types of anesthesia include the following. This type of anesthesia while very safe is the type most likely to cause side effects.
The remaining loss is largely convective which is proportional to the difference between skin and air temperatures multiplied by the square root of air speed. The use of a fan to cool off the body is one example of convection. General where you are asleep Regional spinal and epidural where an entire area is numb and you may also be sedated.
Prevention of vasoconstriction and shivering - blocked sympathetic and motor nerves. To prevent heat loss to the surrounding atmosphere insulation of the skin is necessary as 90 metabolic heat is lost via the skin. Which type of drug is used to treat possible postoperative nausea and vomiting.
Radiative loss is proportional to the difference of the fourth powers of room wall ie. Fully dilated blood vessels lose heat 8 times faster than fully constricted vessels. The type of anesthetic technique selection will be based on various factors including patient factors such as health history and physical examination the type of oral health services being provided and the length of procedure.
Vasodilation below the block. Learn about sedation and general regional and local anesthesia including the differences in how each type works and when each is typically used. Radiant heat loss is responsible for the majority of heat loss.
The other was subjected to one of four warming procedures. 5 Two of the most common vasodilatory drugs used in anesthesia are acepromazine and gas inhalants. General anesthesia A drug-induced loss of consciousness during which patients are not.
All types of anesthesia are administered to keep you comfortable and pain-free during surgery medical procedures or tests. Redistribution of heat from core to periphery. Supplemental heat sources include circulating water blankets electric heating pads and commercial products that can be warmed in a microwave.
Combined general and regional anaesthesia will have a similar effect as the regional. Never place the animal directly on the heat source. But there are some key differences.
Radiation is a form of heat loss through infrared rays. Provide supplemental heat during all anesthetic events. The main types of anesthesia include.
Malignant hyperthermia is a rare complication of some types of general anesthesia. Warm and Cold Thermal afferents blocked along with sensory block. Ambient and skin temperatures.
In awake animals coughing and gagging are protective reflexes which prevent inhaling stomach contents or other foreign materials into the lungs. General anesthesia causes you to lose consciousness. Radiant heat loss may be minimized by wrapping the neonate in a warm blanket and isolating the skin from the cold operating table.
At steady state heat loss must equal this amount. When core heat production heat loss to the peripheral compartment core temperature reaches a plateau. It has agonistic actions on GABA receptors.
The skin particularly of the premature neonate is thinner and has less subcutaneous tissue increasing the rate of evaporative heat loss. One of each pair was a control. The loss of consciousness that occurs during anesthesia is often accompanied by loss of the ability to cough and gag.
Convection is the process of losing heat through the movement of air or water molecules across the skin. Low ambient temperature of the operating theatre. Which type of anesthesia would be considered nontraditional in the United States.
Hyperthermia differs from fever in that the bodys temperature set point remains unchanged. 28 It occurs with the transfer of heat to the environment and is dependent on the temperature differences between the neonate and the environment. Evaporative heat loss from a large surgical incision may equal all other sources of intraoperative heat loss combined Roe 1971.
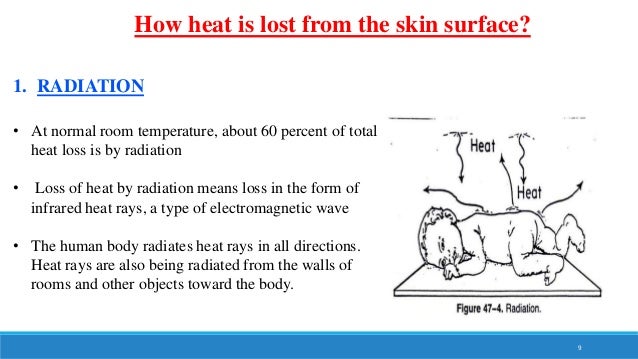
The major cause of loss is radiation accounting for roughly 60 of the total. Impaired thermoregulation secondary to anesthesia.
 Heat Loss An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Heat Loss An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
 How To Prevent Perioperative Hypothermia In The Dog And Cat Causes And Consequences The Veterinary Nurse
How To Prevent Perioperative Hypothermia In The Dog And Cat Causes And Consequences The Veterinary Nurse
 Heat Loss Mechanisms Under Anesthesia Download Scientific Diagram
Heat Loss Mechanisms Under Anesthesia Download Scientific Diagram
 Heat Loss Mechanisms Under Anesthesia Download Scientific Diagram
Heat Loss Mechanisms Under Anesthesia Download Scientific Diagram
Http Www The37company Com Dbdownload 153 Successful Temperature Management Booklet Second Edition English Pdf
 Temperature Humidity Anesthesia
Temperature Humidity Anesthesia
 Heat Loss Mechanisms Under Anesthesia Download Scientific Diagram
Heat Loss Mechanisms Under Anesthesia Download Scientific Diagram
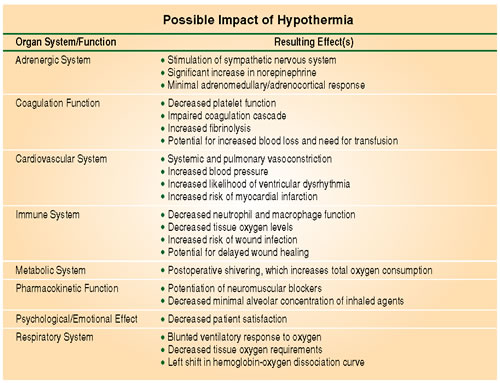 Perioperative Temperature Management Roundtable Discussion Identifies Need To Avoid Hypothermia Anesthesia Patient Safety Foundation
Perioperative Temperature Management Roundtable Discussion Identifies Need To Avoid Hypothermia Anesthesia Patient Safety Foundation
 Temperature Humidity Anesthesia
Temperature Humidity Anesthesia
 Heat Loss An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Heat Loss An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
 Heat Loss Mechanisms Under Anesthesia Download Scientific Diagram
Heat Loss Mechanisms Under Anesthesia Download Scientific Diagram
 Objectives To Recognize The Ways Of Heat Loss In Newborn Baby And Etiology Clinical Features And Management Of Hypothermia In Newborn Baby To List The Ppt Download
Objectives To Recognize The Ways Of Heat Loss In Newborn Baby And Etiology Clinical Features And Management Of Hypothermia In Newborn Baby To List The Ppt Download
 Temperature Humidity Anesthesia
Temperature Humidity Anesthesia
 Phases Of Hypothermia Under General Anesthesia Download Scientific Diagram
Phases Of Hypothermia Under General Anesthesia Download Scientific Diagram
Http Www E Safe Anaesthesia Org E Library 02 Heat Production And Loss Update 2008 Pdf
 Normothermia Management Prevention Of Harm From Perioperative Hypothermia Anesthesia Key
Normothermia Management Prevention Of Harm From Perioperative Hypothermia Anesthesia Key